Comparison of router and bridge
Typically, routers are used to connect geographically dispersed networks together, making it possible to connect a large number of computers together. Before routers became popular, bridges were often used to achieve the same purpose. Bridges perform well in small-scale networks, but in large environments, problems arise. The bridge must remember all the independent computers on the network. The problem with connecting a large number of computers together with a bridge is that the bridge cannot understand the network number, so broadcasts generated anywhere on the network will be sent to every place on the network.
If the PC sends a broadcast packet, it will be sent by the bridge to all network segments
If the PC sends a broadcast packet to net l, the broadcast packet will not be further propagated on the Internet
Many PC network systems widely use the broadcast function, which makes a large amount of available bandwidth in the bridged network consumed by broadcast.
For this, let's compare the routing decisions of routers and typical workstations or hosts in an interconnected network.
A typical workstation (for example, a PC running the currently popular TCP / IP protocol stack) needs some manual configuration before it can work on a TCP / IP network. At least one IP address, one subnet mask, and one default gateway must be configured.
On the workstation, routing decisions configured in this way are very simple. If the workstation wants to send a packet to another computer on the same network, the packet is sent directly to the destination computer. If the destination computer is on a different network, the message packet is forwarded to the default gateway, routed, and finally reaches the destination.
And the best way to route packet packets, you also need to remember the network topology that often changes due to equipment or other failures. To accomplish these tasks, each router maintains a routing table (rouTIng table), which lists all known network numbers and how to reach these networks. Routers also use routing protocols, which keep routing tables consistent with frequently changing interconnected networks.
Coupletech Co., Ltd also supplies water cooled modules, air cooled modules and heat-sink system for high power laser. Usually we need to use all kinds of methods, e.g. water cooling, air cooling and heat sink to make the Laser Crystal, nonlinear crystal and Pockels Cell work normally within specified operating temperature range. Thus we need crystal mounts with water cooling, air cooling or heat sinking.
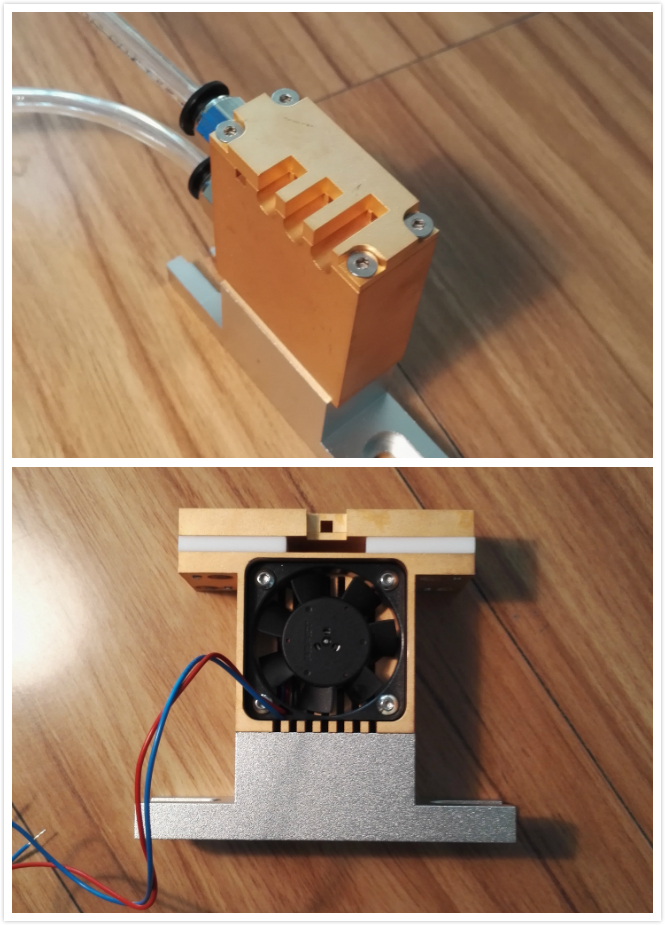
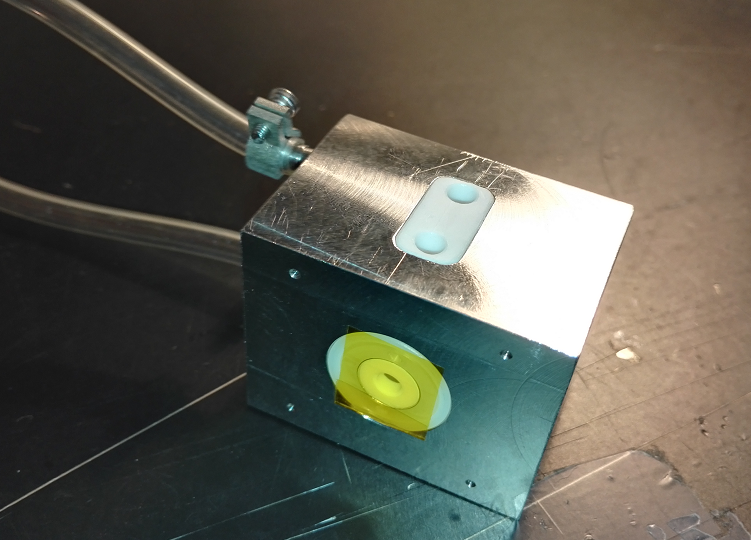
Narrow Aluminium Optical Rail,Narrow Aluminium Rail Carriers,Aluminium Optical Rails
Coupletech Co., Ltd. , https://www.coupletech.com