
For enterprises, big data is essentially a kind of management thinking. Its fulcrum lies in the integration of business information resources and social media, and the integration of internal and external data. On such a pivot point, it reflects on the organizational form, operational paradigm and value creation of enterprises. The model is the true meaning of “big data enterpriseâ€.
A medium-sized department store that records the number of passengers in each area of ​​the mall through video surveillance, thereby assessing the length of the store's time of the passengers at each time of the day, and then using the sales record data to estimate the “search-type†customers with clear purchase targets in the passenger flow. Designed targeted marketing tools and service measures for the proportion of “browsing†customers who do not have a clear purchase target.
The amount of data involved in this practice is not huge from a technical perspective, but the integration and development of multi-source data in the mall is a typical embodiment based on big data management.
In theory, every business can have big data, but not every business can become a big data enterprise.
Big data is named for its “big†size, but volume is not the only feature of big data, or even the most important feature of big data. The huge volume highlights the technical needs. For managers, deliberate pursuit of huge volume of data does not have much practical significance. The more important characteristics of big data are the source and shape of its diversity, the rapid and rapid generation and evolution, and the high level of in-depth analysis. rely. Therefore, the core of the enterprise's control and control of big data is not how large the data is, but whether it can capture and integrate the inrush data from the diversified sources of information inside and outside the enterprise. Analyze and develop its business value.

From a management perspective, big data is neither a technology nor an application system, but rather a management thinking based on internal and external data fusion to improve management efficiency and open up value creation models.
There are two main dimensions of internal company data:
First, data closely related to business functions and processes, such as inventory information, material demand information, production planning information, procurement information, etc., can be collectively referred to as business process information;
Second, the information created, recorded, exchanged and accumulated by employees and various management systems in their daily work and activities, such as communication records among employees, work experience, experience sharing, event news, etc., can be collectively referred to as knowledge and Communicate information.
The development and integration of these two data dimensions has spawned big data within the enterprise. as the picture shows.

Under the joint support of integrated enterprise systems, internal social media, and deep data analytics, Jack Welch's “Borderless Organization†is made possible in a new environment and is endowed with new meaning. Departmental boundaries and hierarchical boundaries are weakened by close business contacts and extensive social connections. Structured business process information is linked to unstructured knowledge and management activity information by multidimensional integration of deep data analysis capabilities. Really have the ability to harness internal big data.
Control corporate external big data
From the perspective of the outside of the enterprise, data resources also include two dimensions:
First, supply chain information directly related to upstream and downstream transactions, such as transaction quotation information, order information, upstream and downstream enterprise inventory and production capacity information;
The second is market and social environment information, such as raw material price trends, market demand and consumer preference information, customer service and satisfaction information.
The basic characteristics of big data outside the enterprise are also reflected in the development of these two dimensions.
The integration of supply chain information integration and socialized business information constitutes the core characteristics of enterprise external big data. Market environment information from social media information sources and supply chain information from inter-organizational information systems, with deep data analysis technology to achieve forecasting and optimization for enterprise business networks, and support real-time, accurate, personalized Based on consumer insight and agile response, it provides rich possibilities for model innovation based on network collaboration and social commerce. Therefore, the management and control of external big data will also become a key way for modern enterprises to occupy a dominant position in the networked business ecosystem and gain operational advantages.
Become a "big data company"
Based on the above analysis, the focus of big data within the enterprise lies in the integration of business process information and knowledge and communication information; the focus of external data of the enterprise lies in the integration of supply chain information with market and social environment information. Furthermore, the basic connotation of enterprise organizations in the era of big data lies in the all-round integration of internal big data and external big data. As shown in Figure 4, big data companies are based on the integration of internal and external business and social media data.
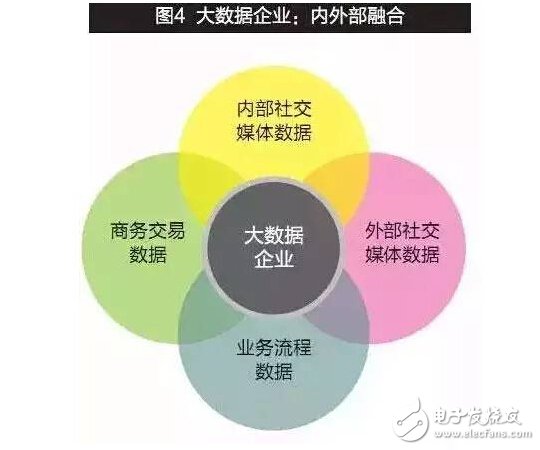
Between these four types of data, companies that are committed to big data management can have two different development strategies.
The first is the integration of social media and business data, in order to quickly identify and respond to changes and opportunities in the internal and external environment through agile response. Under this strategy, real-time data acquisition and analysis methods for high-speed data streams will become the main supporting means of big data management.
The second strategy is to lead the internal and external data fusion, in order to comprehensively collect internal and external information, to accurately predict the medium and long-term development trend, so as to achieve highly optimized business decisions, and obtain the enterprise network through the control of the information environment. Leadership in the ecosystem. Under this strategy, large-scale multi-source heterogeneous data collection, cleaning and integration methods will become the core support of big data management.
How to tap the value of enterprise big data
The value development of enterprise big data is highly dependent on deep data analysis capabilities. From the perspective of internal and external integration, enterprise big data analysis includes three basic dimensions, namely content, relationship and time and space.
The content dimension refers to the information content carried by the data itself. For example, Company G is a large telecom service provider that has built a “team blog†system. On this internal social media platform, more than 3,000 work teams in the company have opened their own blogs to publish and exchange work experience, life experience and other aspects. After several years of development, the entire blog system has accumulated more than 7 million blog posts, more than 15 million comments, and maintained more than 150,000 blog posts per month, with an annual reading volume of more than 10 million. The value development of the large amount of data accumulated by this platform is first reflected in the refinement of its information content. Work-related blog content on the platform, such as customer service cases, experience sharing, etc., after automatic screening classification, topic recognition, and keyword indexing, is built into an enterprise knowledge base to provide fast and effective knowledge support for business and management work. Become a powerful tool for employee training and self-study. A large number of non-work related blog posts and commentary content, including common sense of life, entertainment information, mood expression, soul chicken soup, etc., after intelligent sorting, have become a unique cultural scene of the company, supporting the active in the enterprise. The atmosphere enhances the cultural identity of employees.
The relational dimension refers to the connection between the data and the objects it refers to. In G's team blog, employees' reports, readings, comments, replies, concerns, etc. reflect in detail the intensive and continuous connections between them, and these links are recorded in the database of the platform. . Through in-depth analysis and mining of these relationship structures, G Company has obtained more accurate and in-depth evaluation methods for the influence, cohesiveness and creativity of employees and teams. Further, the behavioral record data of the blog platform and the transaction record data in the business system, as well as the performance data of employees and teams, can also be effectively linked, so that managers have powerful tools to help them discover And understand the potential relationship between employees' behavioral characteristics, job performance, and business ability, and then achieve benign and optimized staffing and talent development.
The space-time dimension refers to the location of data generation and propagation and the pattern of data evolution over time. For G, thousands of business locations are scattered across different cities, so location information in the data is directly relevant to virtualized team collaboration. In addition, the location information also includes the location of the data in the organizational functional structure and hierarchy. At the same time, in the team blog of G Company, the analysis of the temporal evolution of feature topics also provides an effective reference for managers. The tracking of the evolutionary patterns of important business activities and operational concepts in the team blogs effectively reveals the employees' perception, attitude and acceptance process of management concepts.
More in-depth value development comes from the cross-combination of the above three dimensions. For example, the combination of content dimension and relationship dimension enables G to identify the relationship between employees' interest preferences, social traits, job nature, and job performance, and to more accurately identify those scattered among different employees, but Experience, creativity, and opportunity signals with important potential impacts. The combination of content dimension, relationship dimension and space-time dimension enables companies to more deeply understand the different employee traits, knowledge and skills, team characteristics, the distribution of hotspot preferences throughout the organization, and the processes and trends in which these structures evolve over time. This makes it more efficient to schedule and configure these resources.
The analytical needs in these dimensions mainly require three aspects of data analysis techniques to support them.
The first category is the global view technology. For managers, grasping the overall state of big data content is often a basic requirement for developing big data values. However, the volume and structural complexity of big data often far exceeds the information carrying capacity of human cognition. Therefore, an effective technique should be able to extract a sufficiently small set of data from a large amount of data for presentation to the manager and enable this small set to adequately represent the data globally. For example, on G's blogging platform, a "representative blogging extraction" technology can automatically select 10 articles in thousands of blog posts that appear every day. These 10 blog posts represent, to a large extent, the thousands of articles that appeared on the day, fully reflecting the hot spots, and can not ignore the unpopular signals, so that managers can read the articles to understand the overall situation.
The second type of support technology is the association discovery technology, whose goal is to sharply identify the connections between data. For example, when G companies try to integrate data from blog platforms, business systems, and HR systems to analyze employees, team traits, and performance information in a comprehensive manner, the complex potential network of relationships between a large number of data attributes needs to be powerful. The association discovery technique is handled.
The third type of support technology is dynamic tracking technology, which is real-time stream data analysis processing and fast incremental data analysis. All three technologies are in rapid development, but they are not yet fully mature, and they need to be sustained and explored by the academic community and the industry.
Conclusion
In a certain sense, the process of integrating business resource integration with social media is a process of “decentralization of informationâ€. The creation and management of information resources has transformed from a centralized model with operations and operations as the core to a creative model characterized by decentralized creation, free communication, and flexible convergence. On the other hand, the process of internal and external data fusion is a process of “de-boundation of informationâ€. The exchange of information between enterprise departments, the exchange of information between enterprises, and the information of enterprises and market environments are realized in an increasingly diverse and real-time manner.
The impact of such a shift on business organizations and their employees will be multifaceted. Positive impacts may include the emergence of innovation awareness and innovation behavior, the development of employee competencies and skills, the improvement of communication satisfaction, the establishment and accumulation of employee relationship capital, the recognition of employees' identity and belonging to the organization, and the negative impact. This may include distracting employees, excessive arguments, and the spread of negative emotions. Therefore, the process of building a “big data enterprise†will also be a process accompanied by difficulties and risks. In this process, managers need to effectively grasp the balance between long-term and short-term performance of innovation and development, prevent and control organizational risks while promoting big data integration, and carefully consider and redefine internal and external boundaries of organizations. .
In other words, for enterprises, big data is essentially a management thinking. Its fulcrum lies in the integration of business information resources and social media, and the integration of internal and external data. On such a pivot point, it reflects on the organizational form, operational paradigm and The value creation model is the real connotation of “big data enterpriseâ€.
Lifepo4 Cells,Li-Ion Battery,Deep Cycle Lifepo4 Battery,Rechargeable Lifepo4 Battery
Zhejiang Xinghai Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.headwayli-battery.com