Smartphones have become an essential part of our daily lives. Whether we're waiting for a bus, having a meal, or even spending time with someone, it's common to find ourselves glued to our phones. But how much do you really know about your smartphone and the networks it connects to? As a communications engineer, I've always been fascinated by the technology behind these devices, and I hope this article will help you understand more about the secrets hidden in your phone.

1
The logos on your phone
When you turn on your phone, you might notice several small icons next to the signal bars. These symbols represent different network technologies and connection types. Let’s take a closer look at what they mean.
Have you ever wondered what those letters like G, E, 2G, 3G, H, and 4G stand for? They are indicators of the mobile network generation your phone is connected to. Let’s break them down:
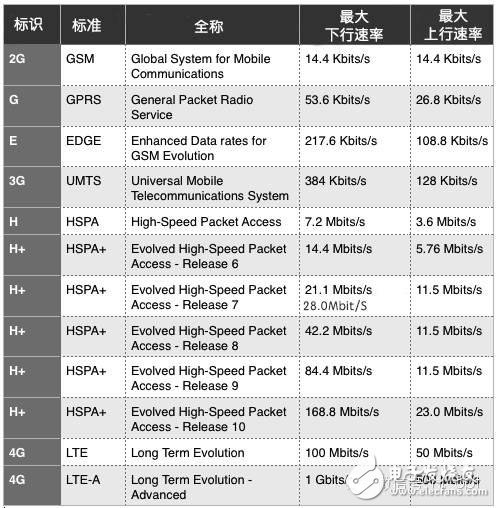
2G, G, and E belong to the second generation of mobile communication. 2G was divided into two main standards: GSM and CDMA. GPRS (G) and EDGE (E) are enhancements of the GSM system. 2G has a maximum download speed of around 14.4 Kbps, while GPRS can reach up to 53.6 Kbps, and EDGE goes as high as 217.6 Kbps.
3G, H, and H+ refer to enhanced versions of 3G networks. The H+ standard can theoretically reach speeds up to 168.8 Mbps, though in practice, it often tops out at around 42.2 Mbps. T stands for TD-SCDMA, which is another 3G standard developed in China.
3G had three main standards: CDMA2000, WCDMA, and TD-SCDMA. UMTS refers to the overall technical specifications of 3G networks, while WCDMA and TD-SCDMA are the air interface technologies used by base stations and mobile devices.
Now that we’ve covered 2G and 3G, let’s move on to 4G and beyond.
2
3.9G – 4G – 4.5G
LTE does not equal 4G. So what exactly is LTE?
LTE stands for Long Term Evolution, a long-term development plan for the UMTS (Universal Mobile Telecommunications System) standard created by the 3GPP (Third Generation Partnership Project). The 3GPP has released multiple versions, from Release-8 up to Release-16, with future releases expected to introduce 5G technology.
The early versions, such as Release-8 and Release-9, are considered 3.9G rather than true 4G. These are commonly referred to as LTE, and their logo looks like this:

Release-10, Release-11, and Release-12 are officially known as LTE-Advanced and are classified as true 4G. Their logo is shown below:

Release-13 introduced LTE-Advanced Pro, often called 4.5G or 4G+. It brings faster speeds and better performance, pushing mobile internet speeds toward 1 Gbps. Its logo is as follows:

We’re now in the 4G+ era, and the future promises even greater advancements with 5G on the horizon.
3
Don’t be fooled by your cell phone signal
Usb Charger,Usb Charger Adapter,Usb Charger Adapter Plug,Usb Port Travel Adapter
Guang Er Zhong(Zhaoqing)Electronics Co., Ltd , https://www.geztransformer.com