In electrical circuits, components such as power supplies and loads are essential parts of the system. A component that does not generate electrical energy is known as a passive component. Passive components can be further categorized into energy-consuming elements and energy-storing elements. Resistors are typical examples of energy-consuming components, while inductors and capacitors are considered energy-storing components. On the other hand, elements like batteries or generators that supply electrical energy to a circuit are referred to as active components or power supply elements.
1. The resistance element reflects the thermal effect of current in a circuit. In real AC circuits, devices such as incandescent lamps, electric furnaces, and soldering irons can be modeled as resistive elements.
(1) Definition of linear and nonlinear resistive elements: A two-terminal element whose voltage-current relationship (VAR) forms a straight line passing through the origin on the u-i plane is called a linear resistive element. The slope of this line represents the resistance R in ohms. If the resistance R remains constant over time, it is referred to as a linear, time-invariant resistive element. When the VAR lies in the first and third quadrants with a positive slope, it is called a linear positive resistive element. Most resistive components discussed in this course are assumed to be linear, time-invariant, and positive resistors. If the VAR of a two-terminal element is a curve that does not pass through the origin, it is classified as a nonlinear resistive element.
(2) Characteristics of the resistive element: A resistor opposes the flow of electric current, exhibiting a property known as resistance. This resistance R determines how much the component hinders the current. Another way to describe this is through the concept of conductance, denoted by G, which is the reciprocal of resistance. Conductance measures the ability of the component to allow current flow, and its unit is Siemens (S).
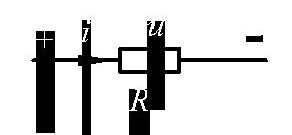
(3) Linear resistance and Ohm’s Law: Since the resistance R is constant for a linear resistive element, the voltage across it is directly proportional to the current flowing through it. This relationship is described by Ohm’s Law. Under the associated reference direction, as shown in Figure 1-4, the mathematical expression is:
U = RI or I = GU (1-9)
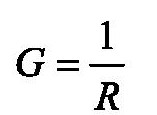
Anti-rat ant Solar Cable is a kind of cable specially used for photovoltaic power generation system, its main function is to prevent small animals such as mice and ants from destroying the photovoltaic line.
The characteristics of anti-rat ant solar cable are as follows:
1. Anti-ant performance: anti-rat ant solar cable adopts special materials and technology treatment, has strong anti-ant performance, and can effectively prevent the invasion of ants and other small animals.
2. Anti-bite performance: anti-rat ant solar cable has good anti-bite performance, can resist the bite of mice and other animals, to avoid short circuit, fire and other safety hazards.
3. Weather resistance: anti-rat ant solar cable is made of high-quality materials, has good weather resistance, and can run stably for a long time under various harsh environmental conditions.
4. Easy installation: The installation method of anti-rat ant solar cable is the same as that of ordinary light cable, without additional tools and equipment, easy and quick installation.
5. Efficient performance: anti-rat ant solar cable has low resistance and high conductivity, which can ensure the efficient operation of photovoltaic system.
In short, the anti-rat ant solar cable is a kind of cable specially designed for photovoltaic power generation system, with the characteristics of ant-proof, anti-bite, weather resistance, easy installation and efficient performance, which can effectively protect the solar cable from the damage of small animals such as mice and ants.
Anti-Mouse Ants Solar Cable,Adapter Cable,Ant Rat Resistant Solar Cable,Ant Resistant Dc Cable
Suzhou Yonghao Cable Co.,Ltd. , https://www.yonghaocable.com