Reading a power supply circuit diagram can be one of the most challenging tasks for beginners. With hundreds of components, it's easy to feel overwhelmed. However, there are some practical tips and strategies that can help you quickly understand the layout and function of a power supply circuit. This article will guide you through key points to consider when reading and interpreting power supply diagrams, with real-life examples to illustrate the process.
A power supply circuit is typically simple in design but widely used in electronic systems. When you first encounter a power supply schematic, follow these steps to break it down and understand its operation:
- Start by analyzing the circuit in the order of "rectification, filtering, and stabilization." This helps you grasp the overall flow of the power supply from input to output.
- During step-by-step analysis, distinguish between the main circuit and auxiliary circuits, as well as primary and secondary components. Understand their functions and required parameters. For example, in a switching power supply, the inductor and freewheeling diode are crucial components.
- Keep in mind that transistors come in NPN or PNP types, and some integrated circuits require dual power supplies. Therefore, power supply circuits often have multiple voltage outputs. Be sure to identify the voltage levels and polarities of each output. Also, pay attention to transistor polarity and electrolytic capacitor orientation during assembly or repair to avoid mistakes.
- Familiarize yourself with common drawing conventions and simplified representations used in power supply schematics.
- Finally, integrate all parts of the circuit from beginning to end to fully understand how the power supply operates.
Example 1: Electric Blanket Circuit
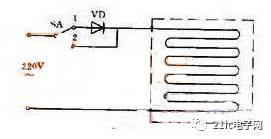
Figure 1: Electric Blanket Circuit
This circuit controls the temperature of an electric blanket. When the switch is in position "1," the AC power is rectified by a diode, resulting in half-wave rectification. The output is a pulsating DC of about 100 volts, which provides low heat. When the switch is moved to position "2," the AC is directly connected to the heating element, creating high heat.
Example 2: High-Voltage Mosquito Killer Circuit
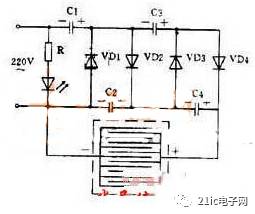
Figure 2: High-Voltage Mosquito Killer Circuit
This circuit uses a voltage doubler configuration to generate a high DC voltage (up to 1100 volts) from 220V AC. This high voltage is applied to a grid, which kills insects when they touch it. The circuit is safe for humans due to its low current. Adding a small light source behind the grid can attract more insects at night.
Example 3: Practical Regulated Power Supply
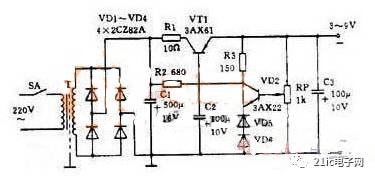
Figure 3: Practical Regulated Power Supply
This is a simple adjustable regulated power supply that provides 3–9 volts at up to 100 mA. Key features include:
- The rectifier bridge may look different, but it’s still a full-bridge configuration.
- It uses a PNP transistor, so the output is negative and the anode is grounded.
- Zener diodes are replaced with two regular diodes for reference voltage, taking advantage of their forward voltage drop.
- A potentiometer is used as a sampling resistor, allowing for adjustable output voltage.
Understanding a circuit diagram doesn’t have to be difficult. By following a systematic approach—starting with the basic stages, breaking down the components, and then connecting everything together—you can quickly grasp the function of even complex power supply designs.
Drop Out Fuse Cutout is a kind of outdoor high voltage protection device, lt is connected with the incoming feeder of thedistribution transformer or distribution lines and primarily used to protect transformers or lines against the impact raised by shortcircuit, overload and switching current. The drop-out fuse cutout is composed of insulator support and a fuse carier, staticcontacts that are fxed on two sides of insulator support and moving contact installed on two ends of fuse carrier, The interior ofthe fuse carrier is the extinguishing tube while the exterior is made of phenolic compound paper tube or epoxy glass.
Composite Fuse Cutout,Cut Out Fuse,Fuse Cutouts Medium Voltage,Dropout Fuse Cutout
Jilin Nengxing Electrical Equipment Co. Ltd. , https://www.nengxingelectric.com