There was a time when the topic of "i3 milliseconds" was being discussed among gamers, with some even joking, "Jinjin: I'm happy?" But now, with the strong rise of competitors, Intel quickly launched its 8th generation Core Duo. The number of cores has nearly doubled across the board, and the performance improvements have been significant, leading to the phrase "i3 can be silent and second." Don’t worry—let’s take a closer look at what’s new this time!

Where is "Coffee Lake" strong?
Coffee Lake is just a literal translation of the name. This 8th generation of Core processors brings a major change—more cores. Now, the i3 features 4 cores and 4 threads, the i5 comes with 6 cores and 6 threads, and the i7 offers 6 cores and 12 threads. This shift marks a huge leap in multi-threaded performance.
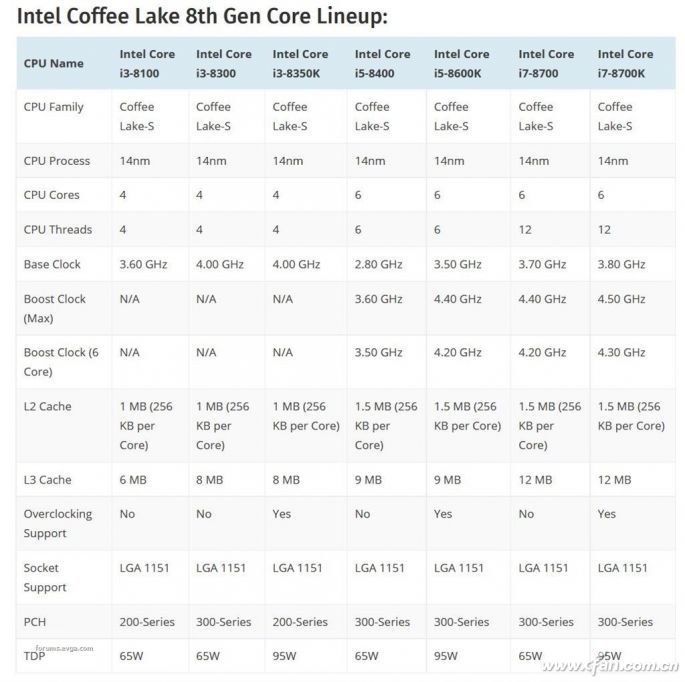
This increase in core count has led to a noticeable performance boost. According to current test results, the new generation shows great improvement in multi-core applications, and single-core performance has also seen a slight rise due to higher clock speeds. Even without other changes, adding more cores naturally leads to better performance. Of course, this wouldn't have been possible without Intel's advanced 14nm process technology (third-generation 14nm).

What is the cost of this upgrade?
Of course, the performance boost doesn’t come for free. Rumors suggest that the prices of these new Core CPUs are expected to be higher than current models. More importantly, they don’t support the 200-series or 100-series motherboards.
Even though they all use the LGA 1151 socket, the pin definitions differ, making them incompatible. This means you’ll need a new motherboard as well. And new motherboards aren’t cheap.
Xiao Bian’s price estimate (don’t blame me if it’s wrong):
8th Gen Core i3 + 300 series motherboard = 1800–2300 RMB
8th Gen Core i5 + 300 series motherboard = 2700–3200 RMB
8th Gen Core i7 + 300 series motherboard = 3500–4500 RMB
And don’t forget about rising memory prices… sigh.
How to choose between i3, i5, and i7?
Looking purely at price, it’s definitely more expensive. But from another angle, it might not be so bad. For the 8th-gen Core CPUs, think of i3 as the previous i5, and i5 as the previous i7. i7 is obviously the strongest. The key point here is the big improvement in multi-core performance, while single-core gains are more modest.
So, budget-conscious users may want to wait and see what the 8th-gen Pentium will bring. Gamers looking for a budget build could still go with 100-series + 7th-gen i5 or i3 7350K, which has excellent single-core performance. For everyday use, an 8th-gen i3 with a 300-series motherboard is a solid choice. For high-end performance, the 7th-gen isn’t worth it anymore—go with the 8th-gen i7.

In the end, Xiao Bian wants to highlight a very interesting CPU—the i3-7360X, newly released. It’s based on the 7th-gen Core architecture and requires an X299 motherboard. It's aimed at overclocking enthusiasts. This dual-core, four-thread processor runs at 4.3GHz, has 4MB of L3 cache, supports dual-channel memory, has a TDP of 112W, and uses the LGA 2066 interface. Its frequency is only slightly higher than the i3-7350K. To be honest, I’m not sure why Intel released this product—it’s quite strange.

A 220V inverter, often referred to as a power inverter, is a device designed to convert direct current (DC) power into 220V alternating current (AC) power. It is commonly used in situations where AC power is not readily available or as a backup power source during power outages. The 220V output voltage is suitable for operating a wide range of electronic devices and appliances, such as laptops, televisions, refrigerators, and power tools.
The main function of a 220V inverter is to perform DC to AC power conversion. It takes the DC power input from a battery bank, solar panel system, or other DC power sources and transforms it into AC power that matches the voltage and frequency requirements of the connected devices. This enables the use of electronic devices that typically run on AC power in off-grid locations or areas with unreliable power supply.
Some 220V inverters produce a modified sine wave output, which is a close approximation of a pure sine wave. While a pure sine wave is the ideal form of AC power, modified sine wave inverters are more cost-effective and suitable for many common electronic devices. However, certain sensitive equipment, such as medical devices or audio equipment, may require a pure sine wave inverter to prevent potential performance issues or damage.
220V inverters come in various types and sizes, including portable inverters that are lightweight and easy to carry, making them ideal for outdoor activities, camping, or powering devices in vehicles. Automotive inverters specifically cater to the power needs of vehicles and can be plugged into a car's cigarette lighter socket.
Efficiency is an important consideration when choosing a 220V inverter. Higher efficiency inverters convert a larger percentage of the DC input power into usable AC power, resulting in less energy wastage and longer battery life.
Overall, 220V inverters provide a convenient and reliable solution for powering electronic devices and appliances when traditional AC power sources are unavailable. They are essential for off-grid living, emergency backup power, and powering electronic devices on the go, ensuring the continuity of electrical power for various applications.

220V Inverter,Industrial Frequency Inverter,3Kw Vfd,Frequency Driver
WuXi Spread Electrical Co.,LTD , https://www.vfdspread.com